Servlet Introduction
Servlet (Example-1)
Life Cycle Events
Con.Ini.Par.(Example-2)
Lif.Cyc.Evt.(Example-3)
Err. & Exce.(Example-4)
Filters (Example-5)
Servlet Hints
Bookmark This Site
|
Introduction to Java Servlets
|
Introduction
|
Early web sites were collections of web pages linked together by Hypertext Markup Language (HTML). Today, websites feature multimedia, e-commerce applications, and other sophisticated web-based applications such as voice over IP and online banking. In addition, there have been advances in web server technologies such as the development of application servers, and dynamic content creation technologies like Java Server Pages (JSP) and Active Server Pages (ASP).
Java Servlets are server side Java programs that require either a Web Server or an Application Server for execution.
1) First you need to instal the JDK 1.5 or j2sdk1.5.0 or above (CLICK HERE for details)
2) Download the server Sun Java System Application Server Platform Edition 8.2 and instal it in the system (CLICK HERE for details)
- To start the server goto Start -> All Programs -> Sun Microsystems -> Application Server PE -> Start Default Server
- To stop the server goto Start -> All Programs -> Sun Microsystems -> Application Server PE -> Stop Default Server
3) Set the PATH and CLASSPATH for java and Sever. (CLICK HERE for details)
|
|
|
Working of Servlets
|
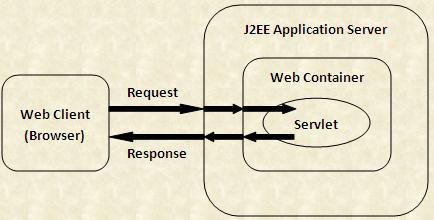
The following figure shows the interaction between J2EE application server and Web container:
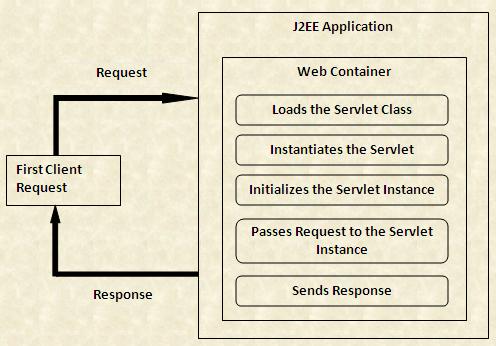
The following figure shows the tasks performed by the Web container when the client request is received for the first time:
|
|
|
Click Next To Continue ...
|
|
|